MLOps Hypertuning flow#
Kiroframe allows you to launch runs with a different set of hyperparameters on cloud instances linked to AWS Data Source. This functionality helps optimize your machine learning workflows by enabling you to test different configurations in parallel, utilizing the cloud's scalability for faster experimentation.
Note
A separate instance is launched for each run.
Warning
Kiroframe launches cloud instances with the configuration defined for your cloud in the solution interface. When the run is completed, the instance will be destroyed.
To use the hyperparameter tuning feature, create a template, then a runset, and launch it.
Note
The AmazonEC2FullAccess policy is required for the user specified in the AWS Data Source connection to use Hypertuning.
First Launch#
Step 1. Create Runset Template#
Since all runs must belong to tasks, you need to create a task first. Don’t forget to create and attach relevant metrics to the task to effectively track performance.
Once the task and metrics are created, it's time to create the runset templates.
Go to the Hypertuning page and click on the ADD button.
Note
Only Organization managers can create runset templates.
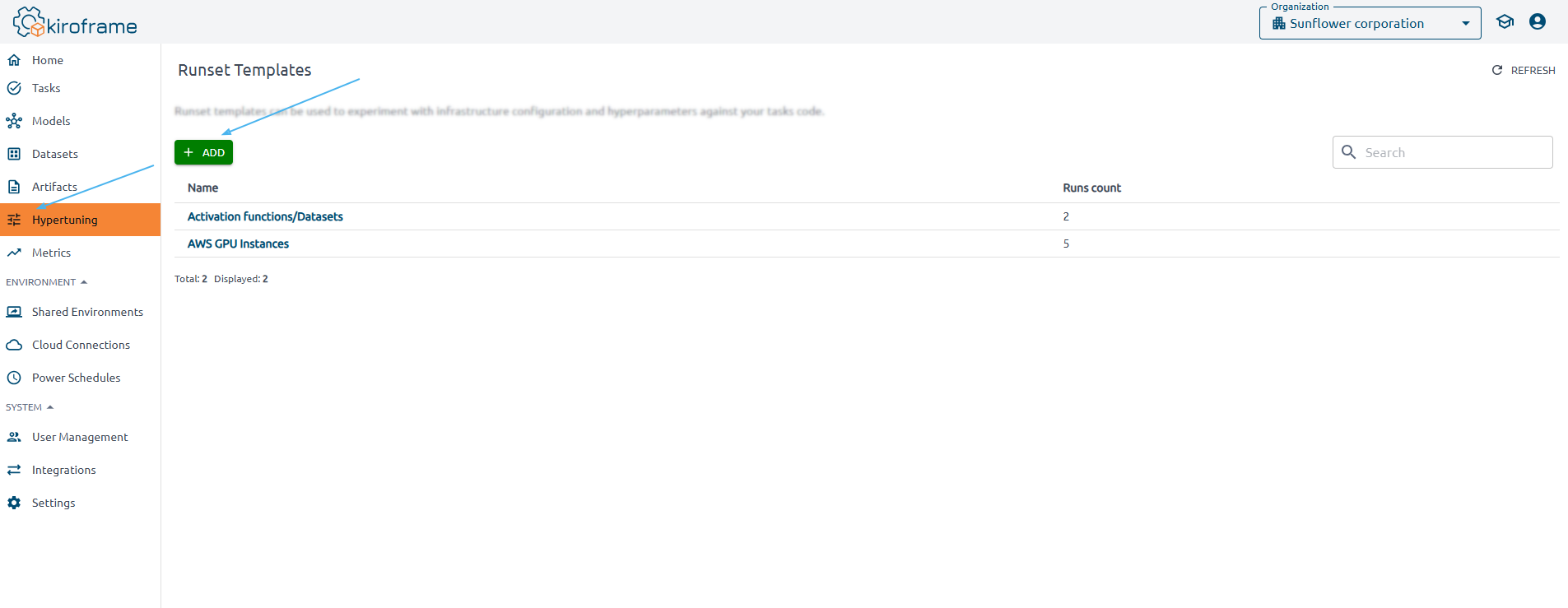
Specify the template information and runset settings:
-
Tasks: a set of tasks to which the created runs belong.
-
Cloud connections: select a cloud connections where the instances are launched and the training takes place.
-
Regions: select regions to launch instances, such as
us-east-1. -
Instance types: select the type of instances on which runs are executed, such as
p3,m5,t3,t2. -
Maximum runset runners: set the value.
-
Resource name-prefix: specify a prefix for all launched instances.
-
Tags for created resources: specify tags for all launched instances.
-
Hyperparameters: specify the name and the environment variable for each learning parameter. For example,
epochs = int(os.getenv('EPOCHS', 5)), whereepochsis the name of the hyperparameter andEPOCHSis the environment variable.Note
Hyperparameter values are set when launching the runset.
Step 2. Create and Launch Runset#
When creating a runset, a single value must be specified for each template parameter: Tasks, Data Sources, Regions, and Instance Types. It is also necessary to set specific values for the hyperparameters and define abort conditions.
Click on the name of the created template.
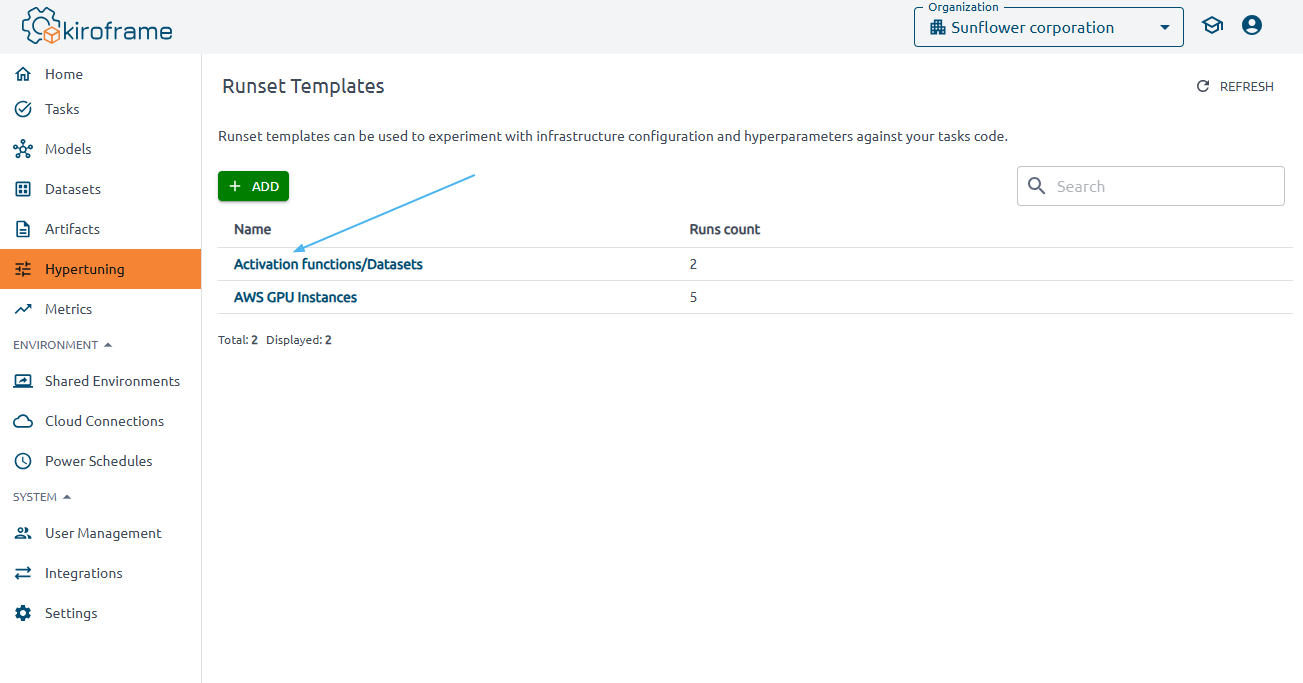
Click the LAUNCH button.
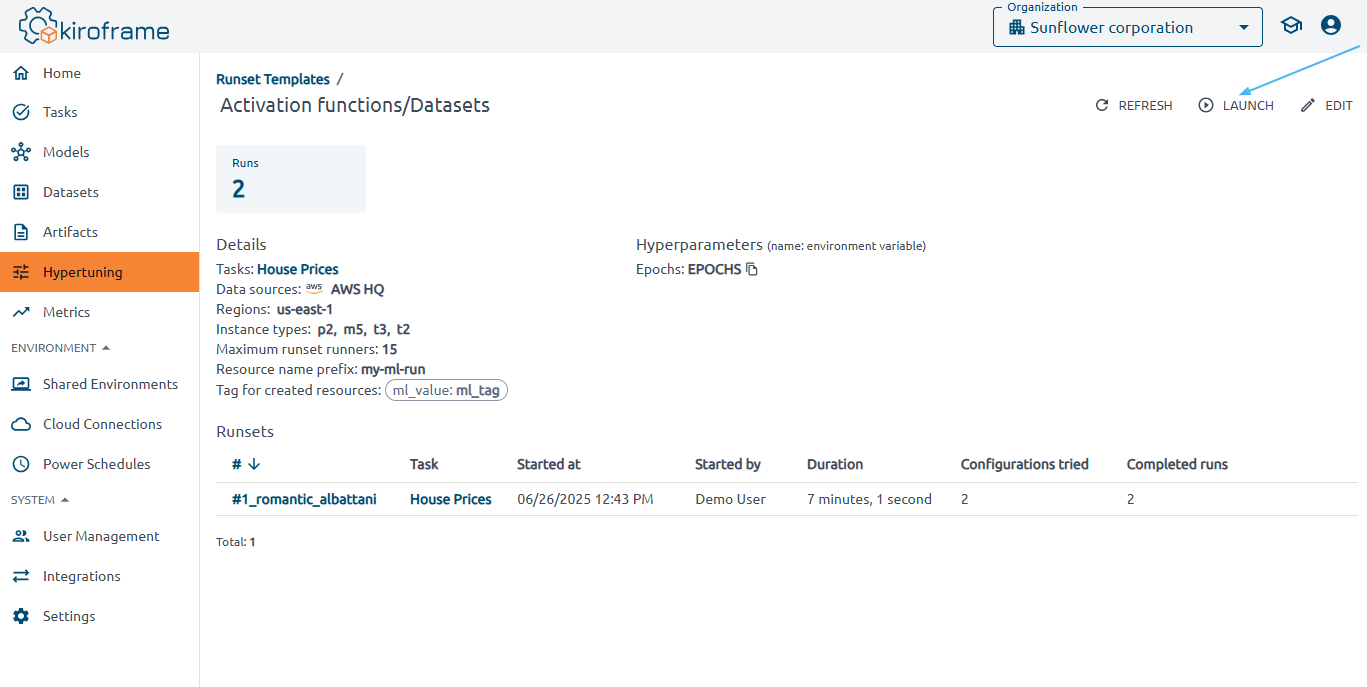
Fill in the fields and click Launch.
Note
If you have already launched runsets for this template, press Fill from latest launch to automatically fill in all fields with data from the most recent runset.
Warning
If you select an instance type that is not supported in the chosen region, an error occurs.
-
Request Spot instances: switch on to execute runs on Spot instances.
-
Max attempts: specify the number of attempts to use a Spot instance before switching back to Pay-as-you-Go.
-
Hyperparameter: enter a comma-separated list of hyperparameter values you want to try with this runset.
Note
The number of runs created is equal to the number of hyperparameter combinations.
Example 1: You have the EPOCHS hyperparameter with values 5, 7, 10, and 20. In this case, 4 runs will be created. In the first run, the EPOCHS parameter will be 5; in the second run, it will be 7; and so on.
Example 2: You have two hyperparameters: EPOCHS (with values 2, 3, and 5) and STATE (with values 3 and 4). In this case, 6 runs will be created. In the first run, the EPOCHS parameter will be 2 and the STATE parameter will be 3; in the second run, the EPOCHS parameter will be 3 and the STATE parameter will be 3; and so on.
-
Commands to execute: specify the commands to run on each executor. They can include setup steps, data preprocessing tasks, task execution processes, or any other operations required for your ML runs. For example,
pip install torchvision==0.13.0 wget https://hystax-eu-fra.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/linear_learn.py -O /home/ubuntu/linear_learn.py python3 /home/ubuntu/linear_learn.py -
Abort conditions: conditions that, when met, cause the runset is completed, even if not all runs was finished.
-
Abort individual run if its duration exceeds: turn on and enter the time in minutes, if the execution of the runs should be interrupted when the time's up. If the condition is met, the runs acquire an 'Aborted' status, and the instances are deleted.
-
Abort runset when one of the runs reaches task goals: turn on, if the runset should be interrupted after the completion of a run, when all its metrics have reached the set goals.
-
View Results#
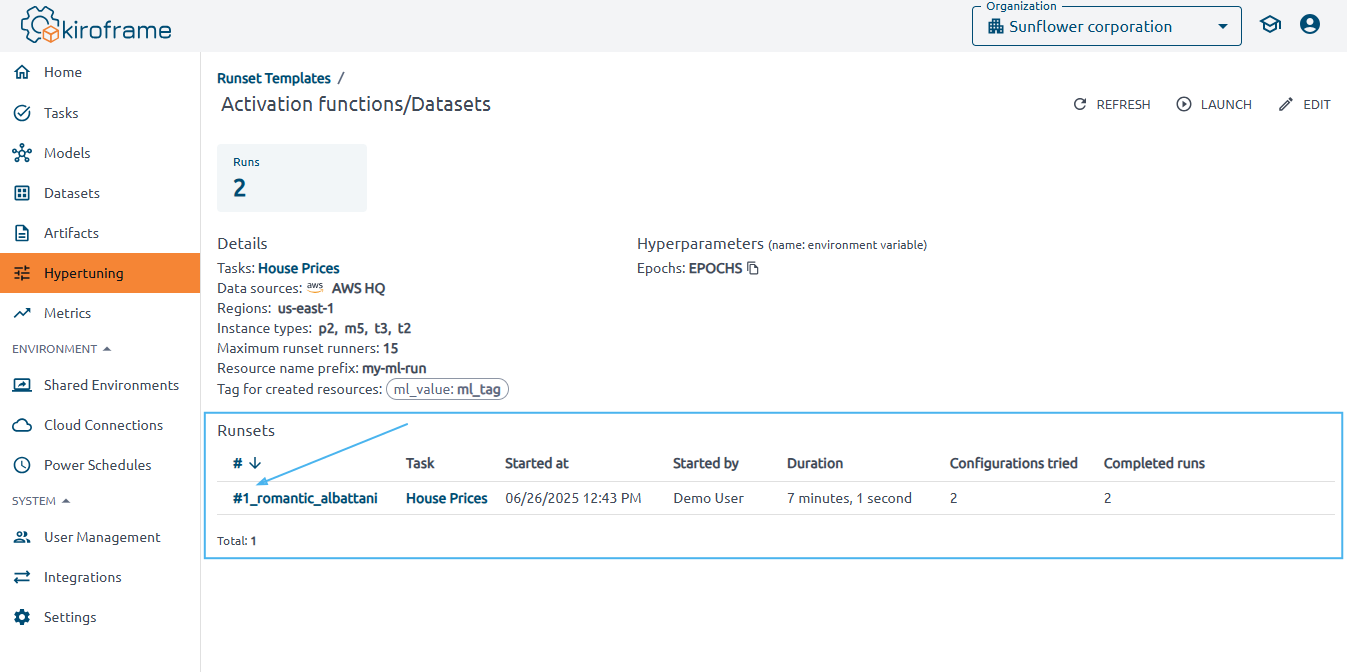
To view the results, click on the template on the Hypertuning page.
Observe configuration details and all runsets launched for the template, along with brief information.
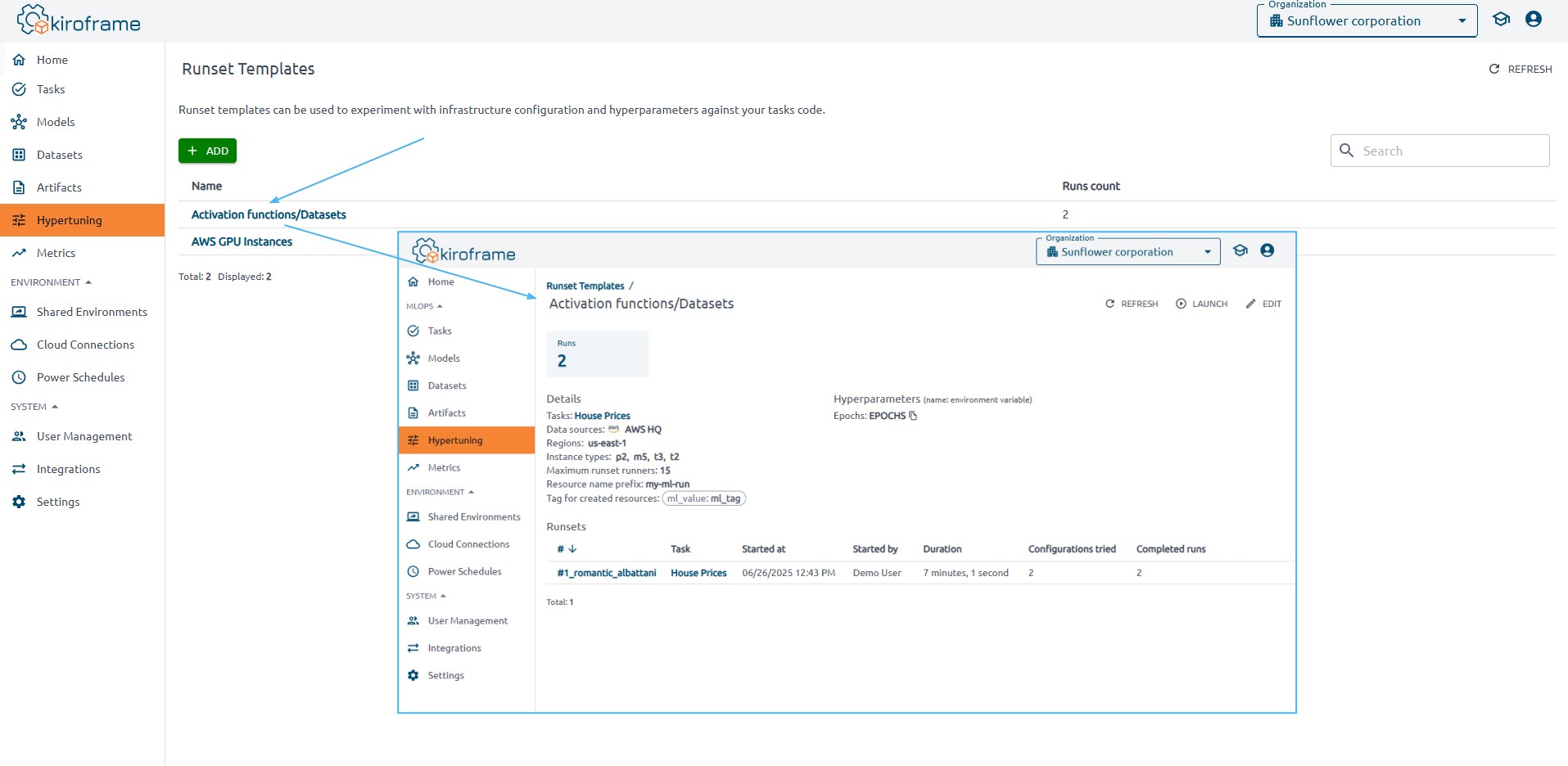
Find summary cards displaying total run counts.
It is easy to get detailed information about each runset. Just click the runset name in the Runsets table.
Runset details, the correlations chart, runset run information, and information about raised instances can be found here.
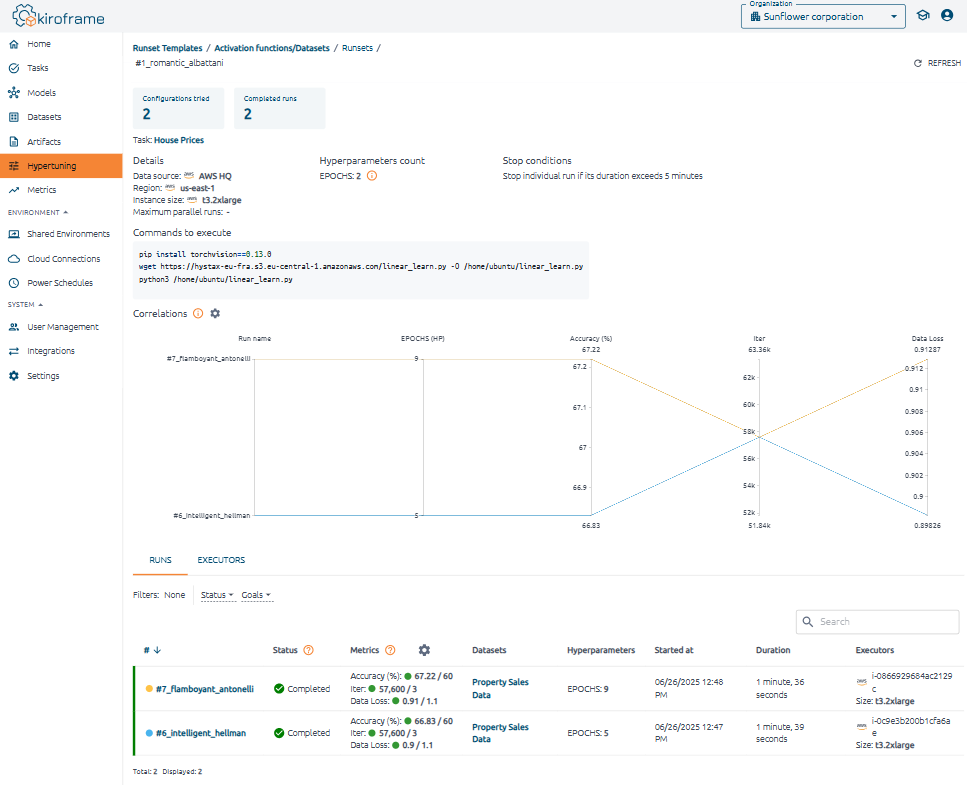
Correlations chart and Runs tab#
The Correlations chart shows the values of hyperparameters and metrics for all created runs. Find all the runset runs under the Runs tab.
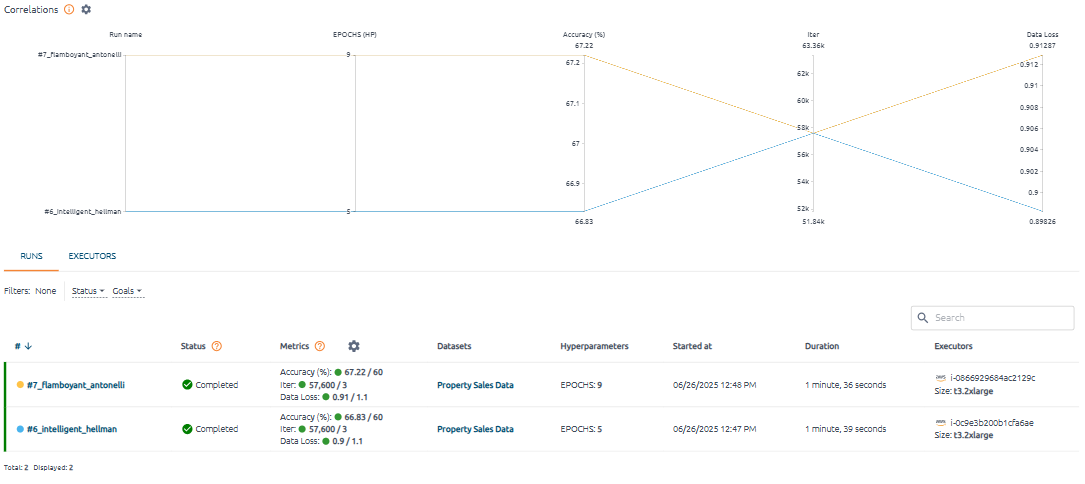
Click the gear ![]() icon next to the Correlations caption of the section to choose which parameters to display.
icon next to the Correlations caption of the section to choose which parameters to display.
The ability to select and highlight specific axis values helps filter the data. Сlick on individual tick marks or dragging across multiple tick marks for an in-depth exploration of the hyperparameters and metrics correlations in the runset.
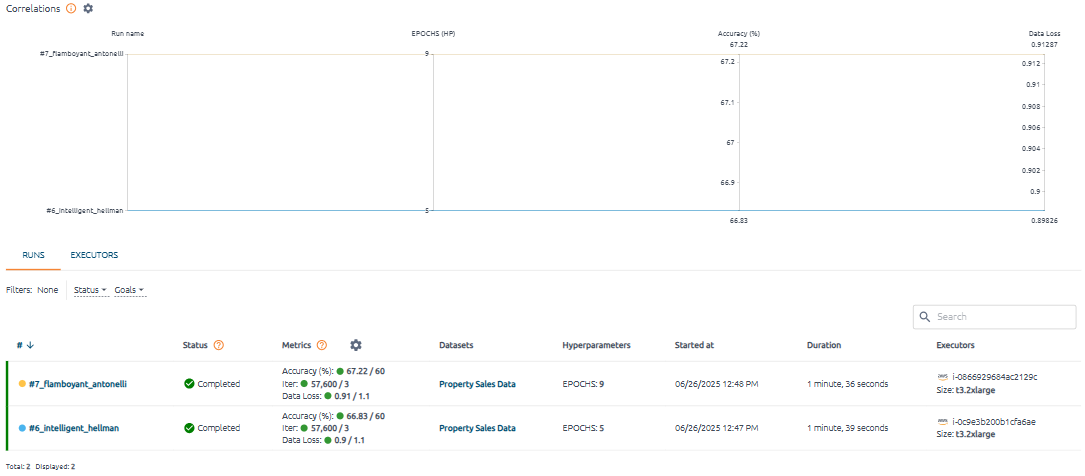
The content of the Runs table depends on the chart and changes when the chart data is updated or filtered.
To clear the selection, press the CLEAR FILTERS button.
Executors tab#
All instances created in the cloud are shown on this tab. Pay special attention to the Status field, as it updates constantly depending on the state of the instance in the cloud.
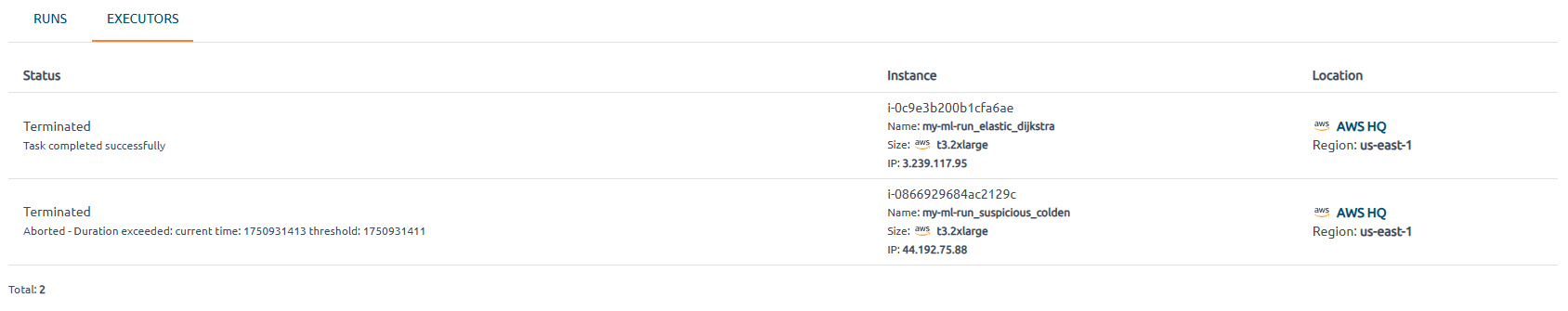
Brief status descriptions:
Terminated – the instance was successfully deleted in the cloud after the successful completion of the run.
Error - the instance was deleted as a result of an abort condition, execution error, or manual stop of the runset. Reasons:
-
Destroy flag is set - one of the runset runs reached its goals. The runset is completed, and all unfinished runs are marked as Aborted.
-
Duration exceeded - the run executed on this instance lasted longer than indicated in the corresponding abort condition.